Outcomes of genetic testing
- Outcomes of testing will depend on the type of testing undertaken.
- All possible outcomes of testing should be discussed with your ordering clinician prior to undertaking testing as part of an informed consent process.
- An infographic explaining these possibilities can be found here.
Possible results may include (but not be limited to):
Pathogenic or Likely Pathogenic
- A definitive explanation for the epilepsy. The change in the gene will affect an individual and cause epilepsy.
- For more information about the next steps after a diagnosis, click here.
Variant of Uncertain Significance
- The effect of the change on the gene is unclear.
- Additional information and evidence may be required in order to work out if this change will cause epilepsy or is a normal variation.
Incidental/Additional finding
- A change in a gene which causes a health issue which is unrelated to the reason for the test.
- Example: finding a change in a gene associated with heart disease, when the reason for testing was epilepsy.
Negative
- There are multiple reasons for a negative result, these include:
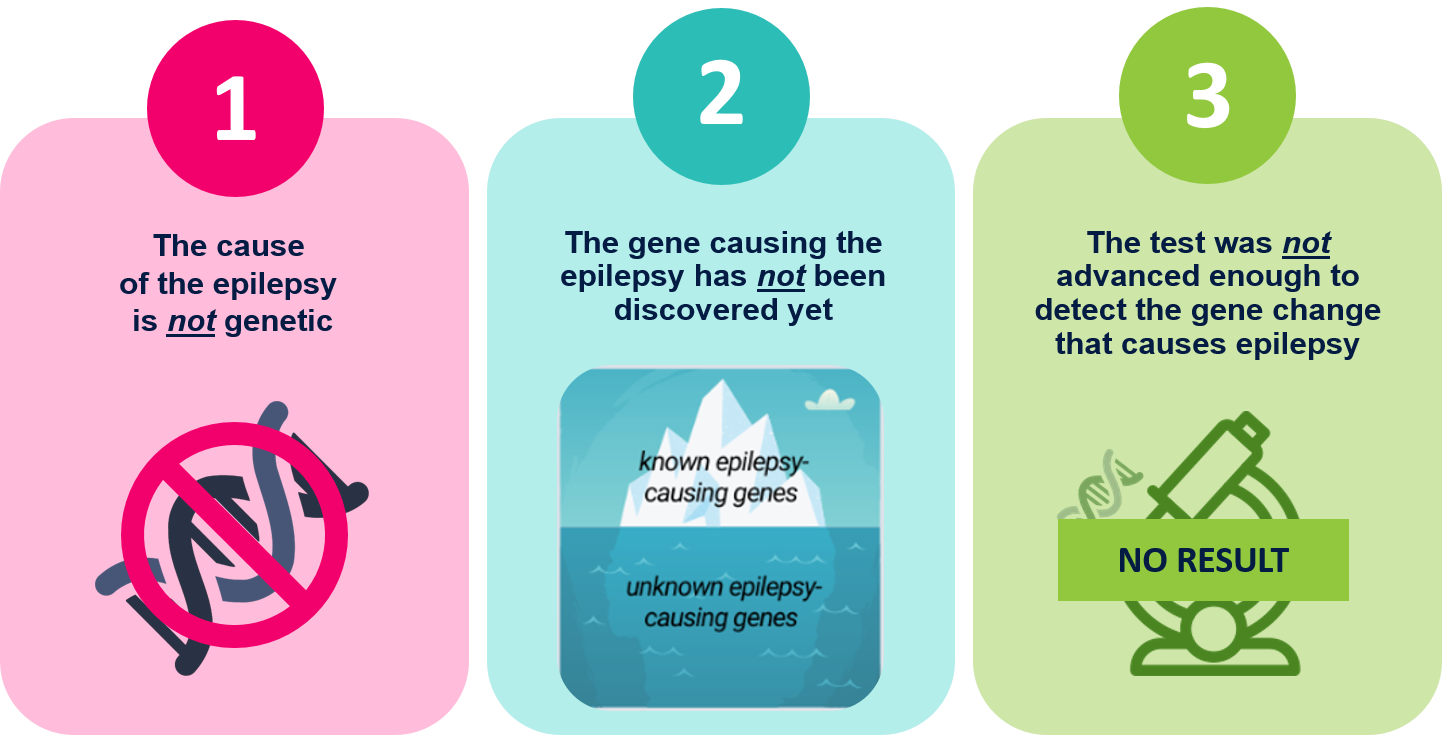
------------
Content on this page was generated via the GeneCompass project. The following article provides more information about the project:
- Robertson EG, Kelada L, Best S, Goranitis, I, Grainger N, Le Marne F, Pierce K, Nevin, SM, Macintosh R, Beavis E, Sachdev R, Bye A, Palmer EE. (2022). Acceptability and feasibility of an online information linker service for caregivers who have a child with genetic epilepsy: a mixed-method pilot study protocol. BMJ Open, 12:e063249. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2022-063249